Why Create Security Architecture Artifacts? |
Security Architecture Strategies |
|
Security Architecture artifacts provide a framework that assists decision makers in their journey towards developing a secure environment for critical business initiatives. There are two risk- based benefits; first, mitigating negative outcomes and second, achieving positive outcomes by enabling the business. Security artifacts help mitigate negative outcomes by guiding the organization towards technology and process decisions that are linked to specific business drivers. Thus, avoiding the trap of procuring technologies that in the most favorable light are just not relevant, yet in many cases can lead to dangerous outcomes. Next, these enable the business by providing a framework that forces the business leaders to think through their operations in more detail. Executives typically do not like surprises and as a byproduct of the process to build these artifacts, business leaders will gain greater insight into their operations and identify potential risks.
|
The security strategy adopts a layered approach with the following themes:
The layered approach ensures the system does not suffer from fragility due to a single event, rather a succession of multiple strategies interconnected to build layer upon layer of defense. Figure 4 below best illustrates this concept by showing how each layer of security is connected to another layer forming the overall security strategy. Figure 4 - Layered Security Model (Sherwood, 2005) |
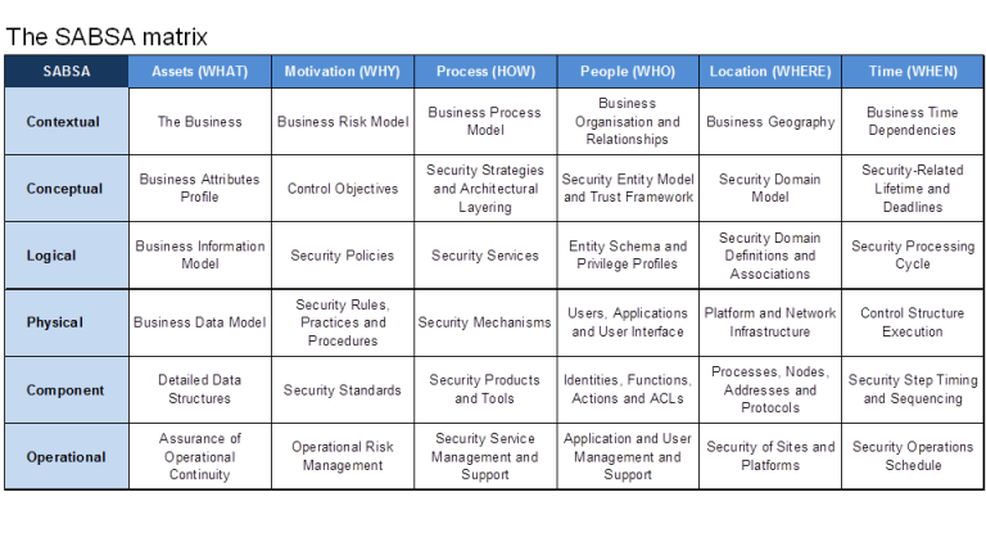
Is there a Standard Industry Model Available?
The SABSA® (Sherwood Applied Business Security Architecture) security architecture model provides a framework for developing a risk-driven, enterprise grade secure architecture (Sherwood, 2009). This is an open standard available for use without licensing. It is composed of frameworks, terminology, models and processes. The underlying methodology presumes a thorough analysis of business requirements where security is concerned. This is expressed in terms of protecting the confidentiality, integrity and availability of business information and providing accountability in information systems. The model contains a series of six cascading levels across a dimension of six vertical cuts, known as the “6 W’s”.
- Assets (what)
- Motivation (why)
- Processes (how)
- People (who)
- Location (where)
- Time (when)